In the age of digital transformation, 10PB cloud storage is now a critical turning point for businesses. But not all cloud storage is the same. IT managers, CTOs, and technology leaders try to decide, will we use “hot” cloud storage or “cold” cloud storage?
Choose the wrong option, and you risk slowing your applications down, running up costs, or disrupting your data-management strategy. This guide will explain some of these differentiators and give real-world use cases for the patterns.
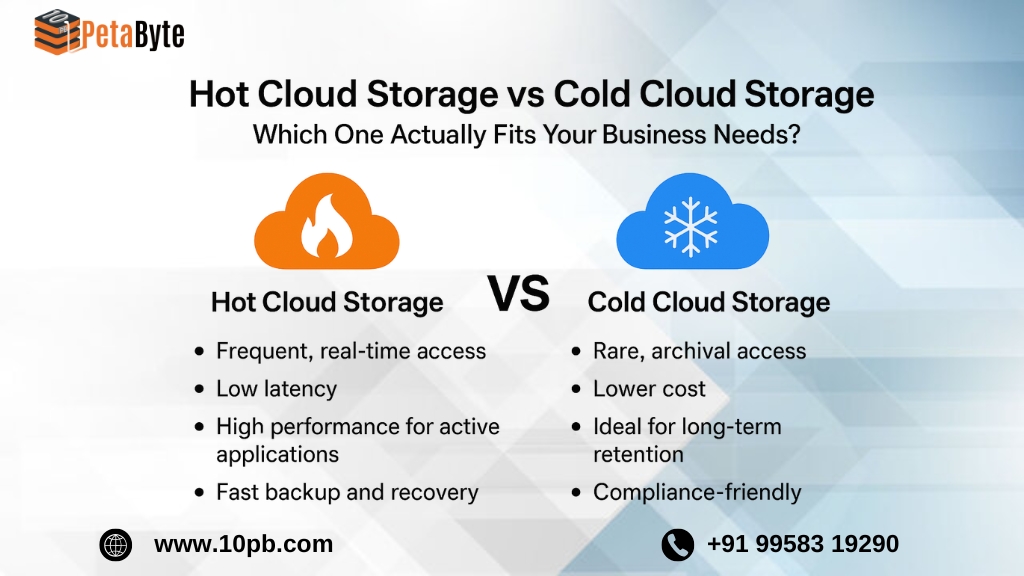
Understanding Hot Cloud Storage
Hot cloud storage provides a solution for data that you frequently need to access. Consider it your “ready to go” consumption storage layer—it is fast, reliable, and purpose-designed for performance workloads.
Reasons businesses access hot storage:
• Immediate access—The data is there whenever you need it.
• Low latency—It performs quickly even with multiple concurrent users.
• Large active workloads—Hot cloud storage is generally better suited for daily SaaS applications and dashboards or real-time analytics use.
• Fast backup/recovery—It recovers data quickly after a failure or disaster.
Hot cloud storage is best used when speed and accessibility can drive meaningful impact on business.
Understanding Cold Cloud Storage
Alternatively, cold cloud storage is suitable for data that you rarely access. It is slower to access, cheaper, and a better option for archival and long-term retention of your documents.
Why would businesses use cold storage?
• Cost savings—cold storage does cost less when dealing with a very large amount of data.
• Compliance—records are maintained securely, and in order to stay compliant with laws and regulations for record-keeping, audit logging can be established.
• Long-term retention—you can archive historical documents or backups that you do not access every day.
Cold storage is a helpful business tool for storing important documents securely at an economical price.
Real-World Use Cases for Hot Cloud Storage
- Active Applications & SaaS Platforms
Giving a fast and simple solution for data access to the CRM, ERP, or customer portals will be the most important thing to guarantee users’ satisfaction.
- Media Production & Collaboration
The large files for instant editing should have very quick access for the team of video editors, designers, and creative professionals.
- Backup & Disaster Recovery
Hot cloud storage allows companies to make full restoration of critical systems in a very short time and thus, their downtime will be very minor.
- AI/ML & Analytics
Data scientists should have large datasets already available to them, and the whole process should be instant for training and analysis reasons.
Real-World Use Cases for Cold Cloud Storage
- Compliance & Regulatory Data
Suitable for the storage of financial records, audit logs, and healthcare data, which needs to be stored for a number of years.
2 Historical Projects & Legacy Files
Cold storage is ideal for older campaigns, archived media, and legacy databases.
- Secondary Backup Copies
An excellent choice for monthly backups or yearly backups that you do not need immediate access to.
- Surveillance & IoT Data
Cost-effective storage of surveillance video footage or data from IoT sensors for long-term access.
Why Hybrid Storage Makes Sense
Most organizations need not limit options to either hot or cold storage. They can use a hybrid storage strategy that provides the benefits of both. Hot cloud storage is for active, frequently accessed data. Cold storage is for archival, compliance, or infrequently accessed data. This hybrid strategy allows businesses to lower costs while still providing performance and the ability to scale to the company’s growth.
FAQs
- What are the key differences between hot and cold cloud storage?
Hot cloud storage is utilized for data that is constantly accessed and requires real-time management. On the other hand, cold cloud storage is meant for data that is infrequently accessed and has the main characteristic of always being at a lower cost.
- What are hot cloud storage’s primary advantages?
- Access to data with immediate effect
- No delay in communication
- Support for demanding applications through high performance
- Quick backup and restoration
- What are cold cloud storage’s core benefits?
- Budget-friendly solution for maintaining data for the long-term
- Regulatory friendly
- Perfect for storing archives and historical data
- Are hot and cold storage compatible with each other in a business setting?
They are indeed. A hybrid approach is hot cloud storage for active data and cold for archival data, which is the way most modern companies implement it.
- Hot storage is the more expensive option as compared to cold storage?
The answer is affirmative; hot storage usually costs more because high performance and immediate accessibility are its main characteristics. Cold storage is the cheaper option for long retention.
Conclusion
IT managers, directors, and CTOs must base their choice of hot cloud storage vs cold cloud storage on data usage patterns, performance requirements, and cost considerations factors from IT’s point of view.
- Having hot cloud storage, active applications, real-time workloads, and backupsare the usages.
- Archival data, compliance records, and seldom accessed files are under cold cloud storage usage.
- A combined approach is suggested to give a good blend of speed, cost, and efficiency.
Cloud storage technology has developed since the very beginnings of the Internet, so now to understand the differences, the benefits, and the practical use cases will help your business in optimizing its cloud storage strategy, reducing costs, and enhancing operational performance—all these without sacrificing security or accessibility.